Namaste! If you are a business owner based in Nepal but operating in the USA, navigating compliance, legal, and beneficial ownership reporting requirements can be a daunting task. From understanding the intricacies of the Foreign Account Tax Compliance Act (FATCA) to ensuring your business is in compliance with the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) regulations, there are many factors to consider.
As a fellow entrepreneur from Nepal, I understand the challenges that come with running a business in a foreign country. In this blog, we will explore the specific requirements and regulations that you need to be aware of to ensure your business operates smoothly and ethically in the USA. Let’s navigate this journey together and ensure your business thrives while staying compliant with the laws and regulations of both Nepal and the USA. Jai Nepal!
Registration Requirements
The United States consists of 50 states and 5 territories, each with its own set of business regulations. To operate legally, businesses must adhere to both state-specific rules and federal laws.
State-Level Registration:
When establishing a business presence in the United States, businesses from Nepal must complete state-level registration in any state where significant business activities occur. This requirement typically applies if your company:
- Has a physical presence in the state
- Frequently meets with clients in the state
- Derives a significant portion of revenue from the state
- Has employees working in the state
Incorporating your Nepali Company in the US
Even if none of the specific criteria apply, a Nepali company must still choose a home state for registration when conducting business in the US. This involves forming a U.S. entity, such as a corporation, LLC, or other business structure, in that state. This registration ensures that the company is officially recognized and compliant with US regulations, regardless of its level of business activity in any individual state.
The newly formed U.S. entity will operate as a subsidiary of the foreign company. This means that while the U.S. entity is legally independent, it remains under the ownership and control of the parent company based in Nepal. This structure allows the company to conduct business in the US while maintaining its international headquarters.
We recommend using Northwest Registered Agent if your foreign company needs to incorporate. They offer expert guidance and can serve as a reliable registered agent for your business, ensuring compliance and smooth operations.
Federal Requirements
In addition to state requirements, Nepali companies must also comply with federal regulations:
- Federal Tax ID: Obtain an Employer Identification Number (EIN) from the IRS. This number is essential for tax reporting and opening U.S. bank accounts.
- Industry Regulations: Companies may need to follow specific federal regulations depending on the industry. For example:
- Import/Export Laws: If the company is involved in importing or exporting goods, it must meet U.S. customs regulations. This includes adhering to rules for tariffs, duties, and necessary documentation.
Beneficial Ownership Information Reporting Requirements
For Nepali businesses conducting operations in the U.S., adhering to Beneficial Ownership Information Reporting (BOIR) requirements is crucial. The Corporate Transparency Act mandates that companies disclose the individuals who own or control them. This applies to most entities, including those that are incorporated or registered in any U.S. state. The goal is to enhance transparency and combat illicit activities such as money laundering and terrorism financing.
A beneficial owner is an individual who controls the company or owns 25% or more of its shares, either directly or indirectly. For compliance with BOIR requirements, businesses must report information about these individuals, including their names, addresses, and identification details. Failure to file this report can result in significant penalties and legal consequences. Therefore, companies from Nepal need to ensure they meet these reporting obligations promptly and accurately.
For your convenience, you can file your Beneficial Ownership Information Report directly on our website. Click here to complete the process in just a few minutes and ensure your business complies with U.S. regulations.
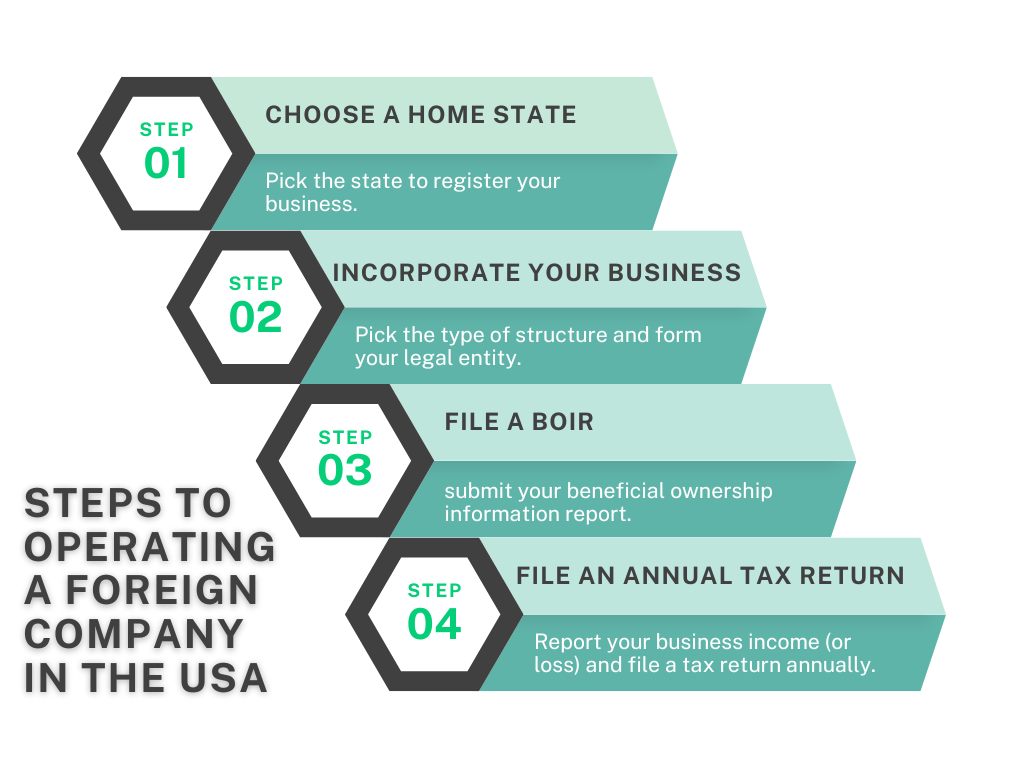
Additional Considerations for Nepali Businesses:
Tax Treaties
As a business operating from Nepal, it’s crucial to understand that there is currently no tax treaty between Nepal and the United States. This absence of a tax treaty means that your company may face potential double taxation on income earned from U.S. sources. Without the protections and benefits typically provided by a tax treaty, your business could be subject to taxation in both Nepal and the U.S. on the same income. It’s essential to carefully consider the tax implications and seek professional advice to navigate this complex situation and minimize your tax burden while conducting business in the United States.
Trade Considerations
When engaging in trade with the USA, businesses from Nepal should be aware of the Trade and Investment Framework Agreement (TIFA) signed between the two countries in 2011. This agreement provides a platform for dialogue on trade and investment issues, but does not offer preferential market access. Nepalese businesses should also familiarize themselves with the Generalized System of Preferences (GSP) program, which allows duty-free entry for certain products from developing countries, including Nepal. However, it’s crucial to note that GSP eligibility can change, so regular updates are necessary. Additionally, Nepalese exporters must comply with US import regulations, including those set by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for food products and the Consumer Product Safety Commission (CPSC) for consumer goods. It’s advisable to consult with the US Embassy in Kathmandu or seek guidance from trade associations for the most current information on industry-specific regulations and requirements.
Your Path to Compliance: Key Takeaways for Nepali Businesses in the U.S.
Operating a Nepali business within the USA requires careful attention to legal obligations, from establishing your home state to incorporating and filing a beneficial ownership report. Meeting these requirements is essential for ensuring compliance and securing your business’s success in the American market. By understanding and adhering to these steps, you can confidently navigate the complexities of doing business in the U.S. and focus on growing your enterprise.
Ready to get started? Click here to file your BOIR in just a few short minutes. We make the process easy, fast, and secure so you can focus on what matters—your business.
Frequently Asked Questions
Have questions about the Beneficial Ownership Filing process? Check out FinCEN BOI Filing's frequently asked questions for the answer.
What is a BOI report?
A Beneficial Ownership Information (BOI) report is a filing required by FinCEN to disclose key details about individuals who own or control a company, ensuring compliance with anti-money laundering laws and enhancing corporate transparency. Filing a BOI takes 5-10 minutes and can be done here.
When does the CTA become effective?
The Corporate Transparency Act (CTA) reporting requirements take effect on January 1, 2024. Business entities established before this date have until January 1, 2025, to meet the reporting obligations.
Are there penalties for not filing a BOI report?
Yes, failing to file a BOI report can result in substantial penalties, including hefty fines and potential legal repercussions. Learn more about the BOI deadlines and non-filing BOI penalties.
How do I file a BOI report?
Filing a BOI takes about 5-10 minutes and can be done here. If you’re not sure if you are required to file, you can take the one minute BOI Eligibility Quiz.
Who is considered a beneficial owner?
A beneficial owner is any individual who either:
- Directly or indirectly exercises substantial control over the reporting company, or
- Directly or indirectly owns or controls 25% or more of the company’s ownership interests.
Substantial control includes the power to direct, influence, or determine significant decisions of the company. This may involve senior officers or individuals with authority to appoint or remove senior officers or a majority of the board.
Ownership interests encompass rights that establish ownership in the company, ranging from basic stock shares to more complex financial instruments.
For more details on “substantial control” and “ownership interests,” refer to our guide on complex ownership structures.
How do BOI reports get submitted to FinCEN?
We submit reports through a secure API connection directly with FinCEN’s Beneficial Ownership Secure System (BOSS). This integration allows for seamless and efficient filing of Beneficial Ownership Information reports, reducing the time it takes to complete and submit a report.
Our user-friendly form is designed to minimize errors by guiding you through the process with clear prompts and checks. Additionally, by using the secure API connection, we ensure that your data remains private and protected throughout the submission process, adhering to the highest security standards.
Who can access the beneficial ownership information?
The beneficial ownership information will be accessible only to authorized government agencies, such as law enforcement and regulatory authorities, for the purpose of combating money laundering, fraud, and other financial crimes.
This data is not publicly available and is used solely for compliance with legal and regulatory requirements. Only those with a legitimate need, as defined by the law, will be able to access this information to ensure transparency and uphold national security.
You can read more about keeping your personal information private when filing your BOIR.
Do I need to file a BOIR annually?
No, you do not need to file a Beneficial Ownership Information Report (BOIR) annually. However, you are required to update and file a new report if there are any changes to the beneficial ownership or company applicant information, such as changes in ownership or control. The report must be filed when there are material updates, but there is no annual filing requirement unless changes occur.
What information is required in a BOI report?
Type of Report
The reporting company must specify the type of report being submitted: an initial report, a correction of a prior report, or an update to a prior report.
Company Information
The reporting company must provide the following details:
- Legal Name: The official name of the company.
- Trade Name: Any “doing business as” (DBA) names used by the company.
- Address: The current street address of its principal place of business. If the principal place of business is outside the U.S., the company must report the address from which it conducts business in the U.S.
- Taxpayer Identification Number (TIN): This includes an EIN, SSN, or ITIN, as appropriate.
Beneficial Owner Information
The reporting company must provide the following details for each beneficial owner:
- Legal Name: The individual’s full legal name.
- Date of Birth: The individual’s date of birth.
- Address: The individual’s residential street address.
- Identification Document: A unique identifying number from an acceptable identification document, the issuing state or jurisdiction, and an image of the document.
Company Applicant Information (if required)
For reporting companies created on or after January 1, 2024, the following information about the company applicant must be provided:
- Address: The individual’s residential street address. If the applicant forms or registers companies as part of their business (e.g., paralegals), the business address can be used. The address does not need to be in the U.S.
- Identification Document: A unique identifying number from an acceptable identification document, the issuing state or jurisdiction, and an image of the document.
Who needs to file a BOI report?
Most businesses are required to file a BOI report, with exceptions for 23 specific categories, such as publicly traded companies and other regulated entities. To learn more about these exemptions and determine if your business needs to file, read this article.
When is the BOI report due?
- Companies formed or registered before January 1, 2024, must file an initial BOI report by January 1, 2025.
- Companies formed or registered in 2024 must file a BOI report within 90 days of receiving actual or public notice of their formation or registration.
- Companies formed or registered on or after January 1, 2025, must file their initial BOI report within 30 days of receiving actual or public notice.
You can learn more about the BOI deadlines here.
What is type of ID is required?
Acceptable identification documents include the following:
- A valid, unexpired driver’s license issued by a U.S. state or territory.
- A valid, unexpired ID card issued by a U.S. state, local government, or Indian Tribe for identification purposes.
- A valid, unexpired passport issued by the U.S. government.
- If none of the above is available, a valid, unexpired passport issued by a foreign government may be used instead.
An identification document must be collected for each beneficial owner.
For companies formed after 2023, an ID must also be provided for the company applicant.
Who is a company applicant?
A company applicant is the individual responsible for creating or registering a company. Specifically, it includes:
- The individual who directly files the document to form or register the entity with the relevant state or tribal authority, such as the Secretary of State.
- The individual primarily responsible for directing or controlling the filing process, even if they are not the one submitting it.
For companies formed or registered after January 1, 2024, this information must be reported as part of the Beneficial Ownership Information Report (BOIR).
Is it necessary to use a certified public accountant (CPA) or other professional to submit a BOI report?
Most individuals will be able to submit their Beneficial Ownership Information reports directly without needing assistance from attorneys or CPAs. Our streamlined, user-friendly form guides you through the process, making it simple to provide the required information accurately and efficiently.
Is a company required to update and correct information that is no longer accurate?
Yes, a company is required to update or correct its beneficial ownership information whenever it is no longer accurate. If there are any changes to the company’s beneficial owners or company applicant information, such as a change in ownership percentages or control, the company must file an updated report with the correct details. This ensures that the information on record remains accurate and compliant with the reporting requirements, helping to maintain transparency and reduce the risk of misuse.
Will I receive a confirmation of submission after submitting the BOIR?
After submitting your BOIR through our website, you will receive an email containing a unique submission process ID, confirming that your submission has been successfully received.
The email will also notify you once FinCEN has accepted your report. In rare instances, if your submission is rejected, we will inform you of the reason and provide a link to resubmit the corrected information.
You can track the status of all your submissions through our BOIR tracking page, ensuring you stay updated on the progress of your report. Most submission have a confirmed acceptance within a few minutes of submission.





